Gas Exchange
Gas Exchange takes place at a respiratory surface
This surface must have:
- large surface area
- thin permeable surface
- moist exchange surface
Gas Exchange in Plants
Gases enter leaf through stomata under leaf
Guard cells enclose stomata and swell to reduce water loss
Gases diffuse through and into mesophyll cells
Diffusion rate increases during day due to photosynthesis:
- oxygen concentration increases
- carbon dioxide concentration decreases
- relative concentration gradients increase… diffusion rate increases
Palisade mesophyll cells are packed with chloroplasts
Palisade cells packed together for maximum absorption
Gas Exchange in Fish
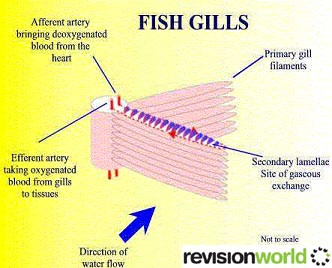
The water surrounding a fish contains a small percentage of dissolved oxygen.
The fish uses a special gas exchange organ (gills).
It has a large surface area and a short distance for gas exchange to the blood capillaries.
Water flows over the filaments, and oxygen can diffuse down its concentration gradient the short distance between water and blood.
Carbon dioxide diffuses the opposite way down its concentration gradient
Approximately 80% of the dissolved oxygen in water is extracted by the gills
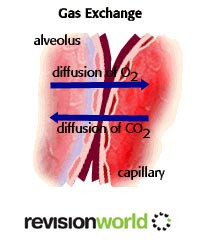
Gas Exchange in Humans
Humans have approximately 600 million alveoli
Walls are two cells thick (easy for oxygen and carbon dioxide to diffuse)
They are constantly moistened by water
They contain phagocyte cells to kill bacteria