Fertilisation
Sperm ejaculated into the vagina
Alkalinity of semen neutralises acidic pH in vagina
Mucus allows sperm to swim through cervix
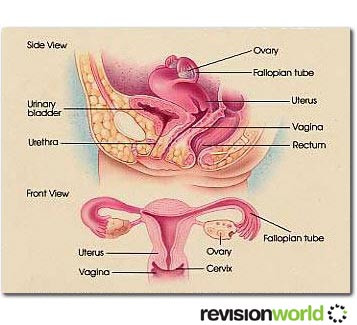
Wall of uterus has two distinct layers
Bulk of uterus wall consists of myometrium (a smooth muscle which expels foetus at birth)
Active muscular contractions during intercourse support sperm
Travel to oviduct in ?5hrs / survival rate of sperm ?48hrs
Endometrium is concerned with anchorage & nourishment of embryo
Sperm acquire ability to fertilise oocyte by removal of acrosome membrane proteins which takes ?6hours
Fertilisation occurs in the fallopian tube, whose walls are lined with ciliated epithelia & contain smooth muscles
Contact between sperm and oocyte is by chance
Image