Reproductive Behaviour
Mammals are either able to breed year round, or in breeding seasons
Gametes are:
- male: small and motile, produced in large quantities
- female: large and less motile, few produced
Gametogenesis:
- male: sperm production = spermatogenesis
- female: egg formation = oogenesis
Female mammals have two cycles: oestrous cycle and menstruation cycle
Oestrous cycle: - ovulation, female is most fertile
Menstruation cycle:
- uterus lining thickens during reproduction cycle
- if fertilisation does not occur, lining breaks down menstruating mammals > discharged as blood through vagina
non-menstruating mammals > reabsorbed, no bleeding
Discharge of blood = menstruation
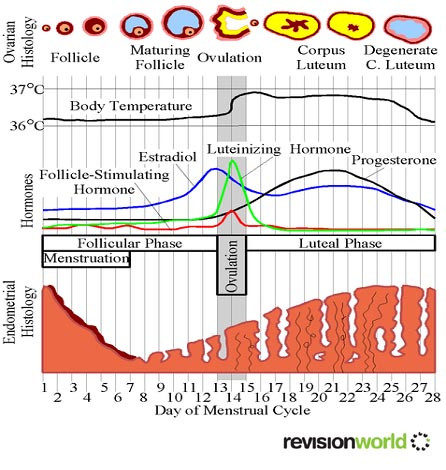
Menstrual Cycle: - controlled by hormones over duration of approx. 28 days
- 3 main phases: follicular, ovulatory, luteal
Follicular: 1st part of menstrual cycle; follicles start to develop into mature female gamete. Follicle cells surround developing egg cell and produce hormones that trigger other responses
Ovulatory: oocyte is released from ovary and passes down fallopian tube into uterus
Luteal: most follicle cells remain after ovulation and continue to develop and form a structure, corpus luteum > more hormones are released