Amino acids
After studying this section you should be able to:
- describe the acid–base properties of amino acids and the formation of zwitterions
- explain the formation of polypeptides and proteins as condensation polymers of amino acids
- describe the acid hydrolysis of proteins and peptides
Amino acids
Image
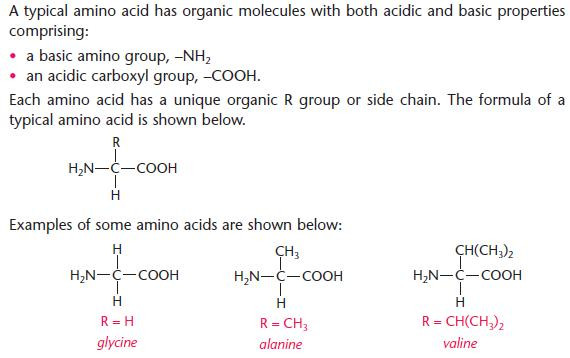
- There are 22 naturally occurring amino acids.
Acid–base properties of amino acids
Image
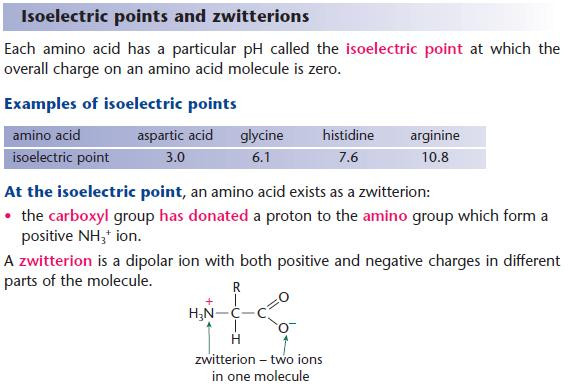
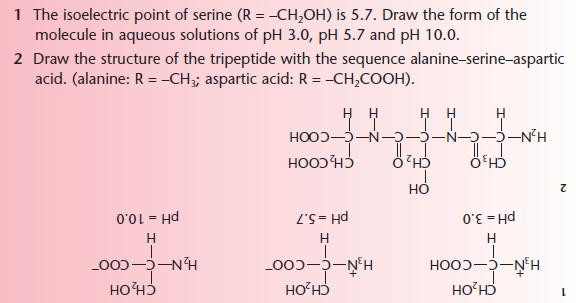
- At the isoelectric point, the amino acids exist in equilibrium with its zwitterion form.
Image
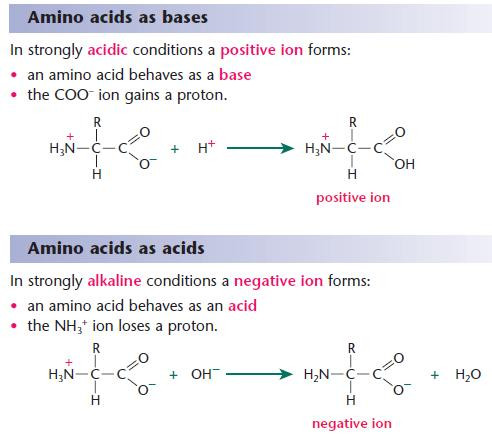
- Because of their reactions with strong acids and strong bases,amino acids act as buffers and help to stabilise the pH of living systems.
Image

Physical properties of amino acids
Image

Polypeptides and proteins
Image
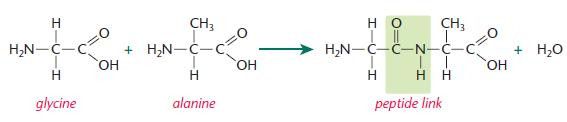
Each peptide link forms:
- between the carboxyl group of glycine and the amino group of alanine
- with loss of a water molecule in a condensation reaction.
Further condensation reactions between amino acids build up a polypeptide or protein.
- For each amino acid added to a protein chain one water molecule is lost.
- Most common proteins contain more than 100 amino acids.
- Each protein has a unique sequence of amino acids and a complex three-dimensional shape held together by intermolecular bonds including hydrogen bonds.
- A polypeptide is the name given to a short chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A protein is simply the name given to a longchain polypeptide.
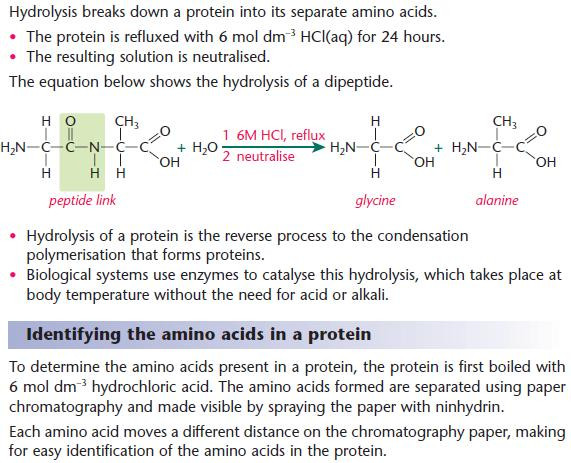
Hydrolysis of proteins
Image
PROGRESS CHECK
Image