Dynamic Equilibrium
Many reactions are reversible. This means the products can react to make the products..
A chemical equation showing this is of the form:
NH4Cl NH3 + HCl
The symbol shows the reaction is reversible.
Dynamic Equilibrium
In a reversible reaction as the products are used up the forward reaction slows and as more product is formed the reverse reaction speeds up. After a while the forward and reverse reactions will occur at the same rate.
The amount of reactants and products won't be changing (This does not mean that there are equal amounts of products and reactant though.) so it will seem like nothing is happening. This is called Dynamic Equilibrium.
It can only happen in a closed system at a constant temperature.
Factors affecting equilibrium
By opening up a closed equilibrium system conditions can be changed after which the system can be allowed to reach a state of equilibrium again.
Factors to change include:
-
Changing the concentration of a reactant or product.
-
Changing the pressure of a gaseous equilibrium.
-
Changing the temperature.
Le Chatelier's principle, says that when a system at equilibrium is subjected to change then the system readjusts itself to (partially) counteract the effect of the applied change and a new equilibrium is established.
This allows a prediction of the effect on the equilibrium position of any change.
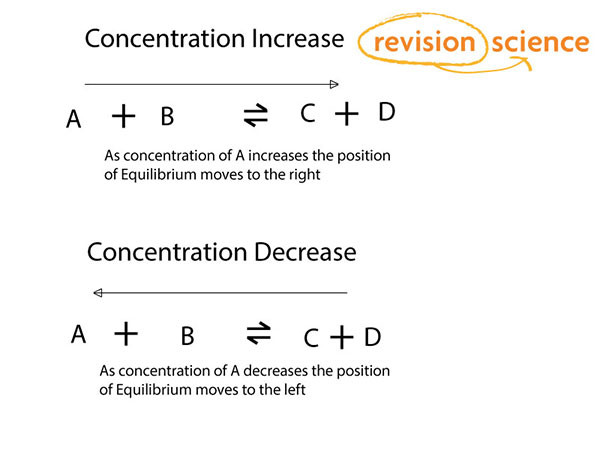
Concentration Changes
If the amount of reactant is increased the amount of product is increased (thereby removing reactant) in order to maintain equilibrium.
If the amount of reactant decreases the amount of product also decreases.
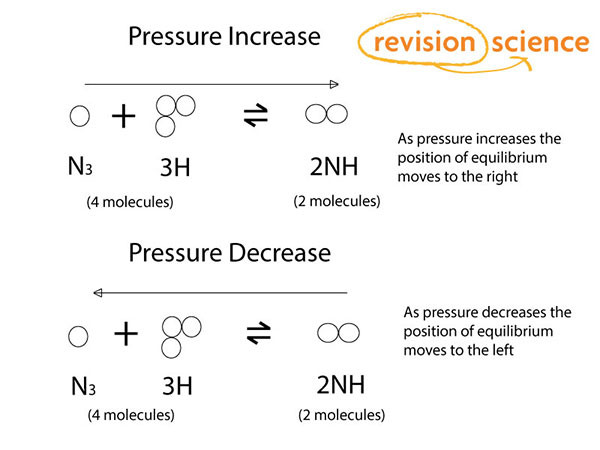
Pressure Changes
The direction of change is dependent on the total number of gas molecules on each side of the equation.
If the pressure is increased the side with the least amount of gas molecules will have an increase in the amount of molecules created.
If the pressure is decreased the side with the most gas molecules will find the amount of molecules created will increase.
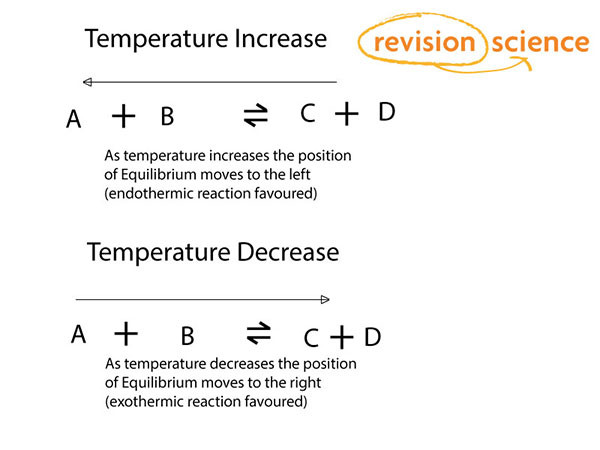
Temperature Changes
If the temperature is increased the position of equilibrium will move to bring it down again – the reaction will attempt to absorb heat.
If the temperature is decreased the position will move to produce heat.
The effect of a Catalyst on Equilibrium
A catalyst will not move the position of the equilibrium state but will help speed up the reactions to reach it.
This video explains about Dynamic Equilibrium
