Answer
Antibiotics affect the behaviour and biochemistry of bacterial cells.
(i) Give THREE ways in which antibiotics affect bacterial cells.
3 from:
Inhibit protein synthesis/ translation/ transcription;
Inhibit DNA replication;
Inhibit cell wall formation/ osmotic lysis;
Disruption of cell membrane function;
Reject destroy cell wall / digest cell wall
[ 3 ]
(ii) Antibiotic drugs are not given for viral illnesses. Give TWO reasons why this is the case.
Viruses have no metabolism / do not need nutrients / no ribosomes / named organelle / cell wall / not living; Antibiotics only active against (living) cells / viruses acellular; Viruses inside cell;
[ 2 ]
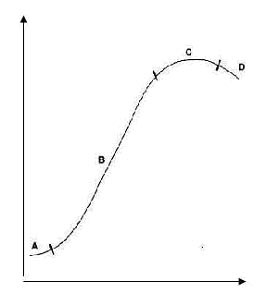
(iii) The graph below describes the growth curve of a population of bacteria. Identify ON THE GRAPH the stages shown by the letters A, B, C and D on the graph.
time
A = Resting Phase or acceptable equiv.
B = Exponential Phase
C = Stationary Phase
D = Death Phase
[ 4 ]
(iv) With reference to the graph, explain the shape of the curve
6 of:
A - equilibrating to / environment / getting used to / conditions; so no [overall] growth so almost straight curve; B - growth phase / doubling phase; numbers increase exponentially; so steep upward curve; C - growth at steady rate; no exponential increase in numbers; so levelling of curve; D - nutrients depleted so numbers fall; build-up of toxins; from dead cells causes growth rate to cease and cells to die; so steep downward curve.
[ 6 ]
[ Total: 15 ]
