Energy Transfer in Circuits
Charge
Unit: Coulomb, C
“The coulomb is the charge that flows past a point when a steady current of 1A passes for 1 second.”
Drift Velocity
The electrons in a current have an overall motion at low speed in a direction negative to the positive.
The three things that affect the drift velocity are:
• Current, I
• Charge carrier concentration, n: number of charge carrying electrons per unit volume
• Cross sectional area of material, A
For a metal: I = n A e v e = electronic charge
For a non-metal: I = n A q v q = ionic charge
Alternating Current and the Oscilloscope
Alternating and Direct Direct
A current from a battery is direct current, d.c., while mains electricity is alternating current, a.c.
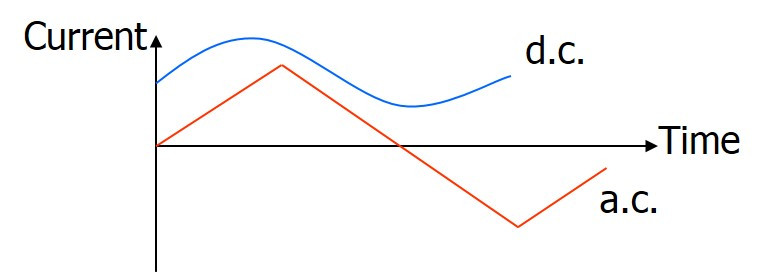
a.c. changes direction, while d.c maintains the same direction even though the current value may vary.
