Transport in Plants
This section covers transport in plants, covering transpiration, the transpiration stream, how to measure the rate of transpiration, factors affecting the rates of transpiration and how stomata open and close.
Transpiration
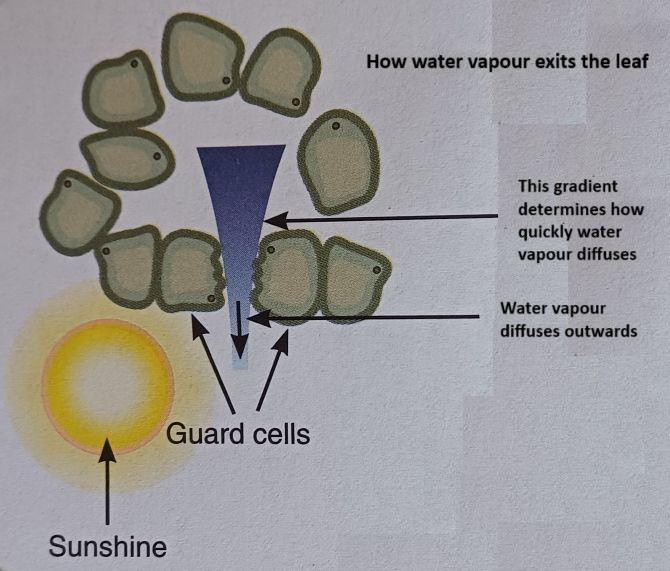
Transpiration is the loss of water vapour from a plant’s leaves, mainly through the stomata. It is a passive process driven by evaporation and diffusion.
The Transpiration Stream
- Water is absorbed by root hair cells from the soil.
- Water travels up the plant through the xylem vessels.
- Water evaporates from the mesophyll cells into air spaces in the leaf.
- Water vapour diffuses out of the stomata, creating a continuous flow.
Measuring the Rate of Transpiration
A potometer is used to measure transpiration rate by recording the uptake of water by a plant.
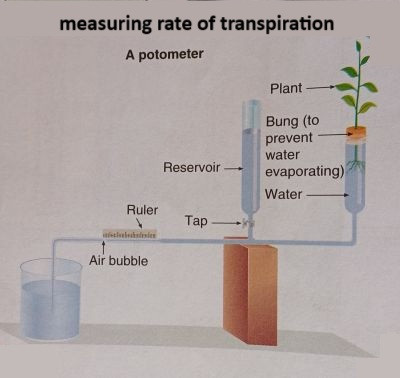
Using a Potometer:
- A plant is placed in a sealed system containing water.
- As water is lost from the leaves, more water is drawn up through the xylem.
- The movement of an air bubble in the capillary tube is used to measure the rate of water uptake.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Transpiration
Several environmental factors influence how quickly a plant loses water:
| Factor | Effect on Transpiration |
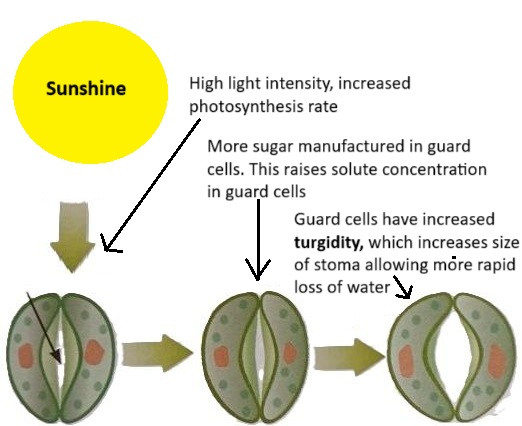
| Light Intensity | Increases transpiration as stomata open for photosynthesis. |
| Temperature | Increases transpiration as water evaporates faster. |
| Humidity | Decreases transpiration as the air is already moist, reducing diffusion. |
| Wind Speed | Increases transpiration by moving water vapour away from the leaf surface. |
Opening and Closing of Stomata
Stomata are tiny pores on the underside of leaves that regulate gas exchange and water loss.
How Stomata Open and Close:
- Open: When guard cells absorb water by osmosis, they become turgid, causing the stomatal pore to open. This happens during the day to allow photosynthesis.
- Close: When guard cells lose water, they become flaccid, closing the stomata to reduce water loss, especially at night or during drought conditions.
Transpiration plays a vital role in transporting water and minerals in plants. The rate of transpiration is influenced by environmental factors, and stomata regulate water loss to prevent dehydration while allowing gas exchange for photosynthesis.
