An Allele is an alternative form of a gene (one member of a pair) that is located at a specific position on a specific chromosome.
Alleles are dominant or recessive
Homozygous = two same alleles (purebred)
Heterozygous = two different alleles
Dominant + recessive > dominant
Dominant + dominant > dominant
Recessive + dominant > dominant
Recessive + recessive > recessive
Example
A heterozygous brown-eyed father and a blue-eyed mother
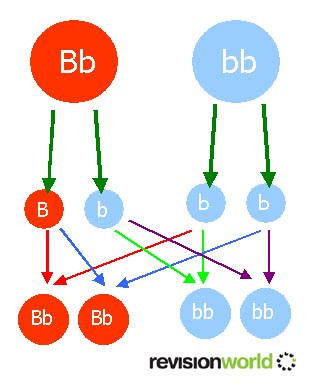
Result: 50:50 chance of being either brown eyed or blue eyed.
An individual is homozygous for a certain gene if they have two identical alleles. They are heterozygous for a certain gene if they two different alleles.
The genotype is the genetic makeup of an individual. For example, it is the particular combination of alleles
The phenotype is the characteristics expressed by an individual. For example, it is the actual eye colour
Monohybrid Cross
In a monohybrid cross two plants or animals, which differ at only one gene and which are bred together.
By looking at alleles of the genes that the parents have we can tell how the offspring will turn out. This can be very useful when carrying out selective breeding of plants or animals.
In humans with inherited diseases it is extremely useful to know about the alleles since we can inform them about the likely effect if they want to have children.
Thsi video below explains about Monohybrid crosses and Punnet Squares

