Hormones help to regulate metabolic processes in the body. Hormones are secreted into the blood through endocrine glands
They travel in the blood to organs where they take effect. The diagram below shows the endocrine system
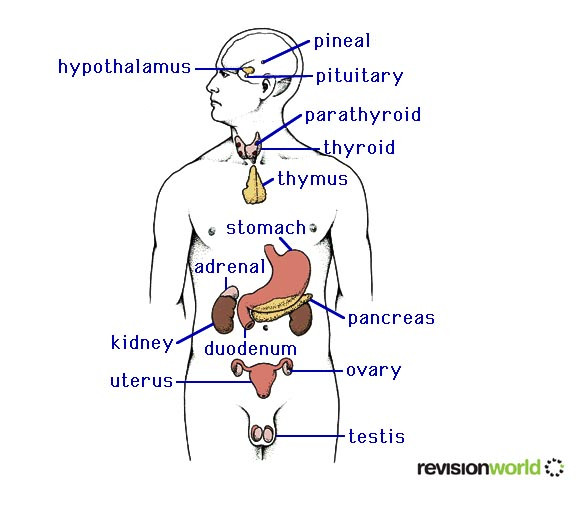
Hormone Reference Chart
| Gland | Hormone | Target organs | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| adrenal gland | adrenalin | vital organs, eg liver and heart | Prepares body for action - 'fight or flight'. |
| ovary | oestrogen | ovaries, uterus, pituitary gland | Controls puberty and the menstrual cycle in females; stimulates production of LH and suppresses the production of FSH in the pituitary gland. |
| ovary | progesterone | uterus | Maintains the lining of the womb - suppresses FSH production in the pituitary gland. |
| pancreas | insulin | liver | Controls blood sugar levels. |
| pituitary gland | anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) | kidney | Controls blood water level by triggering uptake of water in kidneys. |
| pituitary gland | follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) | ovaries | Triggers egg ripening and oestrogen production in ovaries. |
| pituitary gland | luteinising hormone (LH) | ovaries | Triggers egg release and progesterone production in ovaries. |
| testes | testosterone | male reproductive organs | Controls |
This video explains more about Hormones and the effects they have
Example: The Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is a recurring cycle of physiological changes in women associated with reproductive fertility.
Four hormones are involved: Oestrogen, Progesterone, FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone ) and LH (Luteinising hormone )
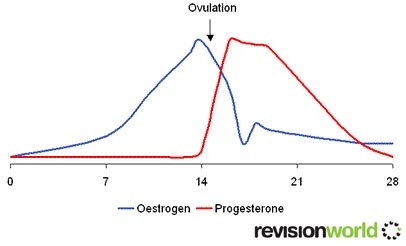
Key stages
1. The egg ripens in the ovaries - stimulated by FSH
2. Womb lining builds-up - stimulated by Oestrogen
3. Egg is releases - stimulated by the LH (about day 14)
4. Maintenance of uterus lining - stimulated by progesterone
5. Uterus lining breaks down - caused by low levels of oestrogen and progesterone
6. Blood and tissue loss (menstruation)
