The Arrangement of the Periodic Table
The Periodic Table
All the elements of the periodic table are arranged in order of increasing atomic (proton) number. The table was named the periodic table because similar properties occur at regular intervals.
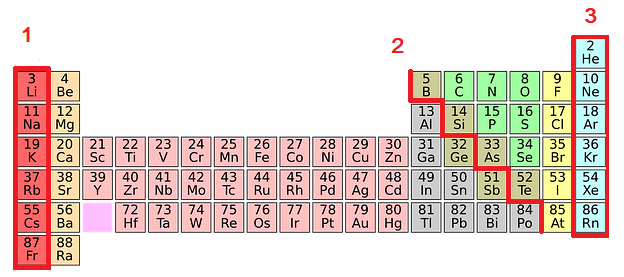
- Elements with similar properties are in columns called groups.
- Elements to the left of this line are metals.
- Elements in the same group of the periodic table have the same number of electrons in their outer shell. This gives them similar chemical properties.
Development of the periodic table
Early attempts to classify the elements involved placing them in order of their atomic weights. This resulted in incomplete tables and the placing of some elements in inappropriate groups based on their chemical properties.
The Russian Chemist Dmitri Mendeleev’s solution was to leave some gaps for elements that he correctly predicted were yet to be discovered. He also reordered some elements based on atomic weights. Increased understanding of isotopes made it possible to explain why the order based on atomic weights was not always correct.
Metals and non-metals
Metals are elements that react to form positive ions.
Elements that do not form positive ions are non-metals
Properties of metals and non-metals
Metals
- Have high melting or boiling points
- Conduct heat and electricity
- React with oxygen to form alkalis
- They are shiny
- They are malleable and ductile
Non-metals
- Have a low melting or boiling points
- They are thermal or electrical insulators
- They react with oxygen to form acids
- They are dull
- They are brittle
The video below explains the arrangement of the periodic table
