Halogens: Group 7 of the Periodic Table
The Halogens
Group 7 of the periodic table is home to the Halogens.
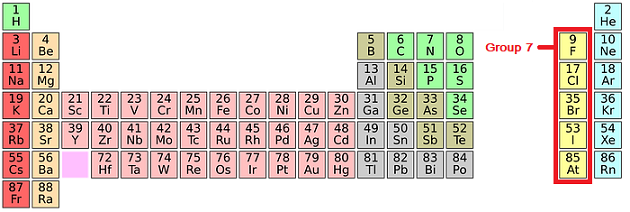
The halogens have the following properties:
- They are non-metals.
- They consist of molecules made up of two atoms (diatomic molecules).
- They react with metals to form ionic compounds where the halide ion has a charge of -1.
- They form molecular compounds with non-metals.
- They form hydrogen halides, which dissolve in water, forming acidic solutions.
More about halogens
Fluorine (State of matter at room temperature) Gas (Colour) Yellow
Chlorine (State of matter at room temperature) Gas (Colour) Green
Bromine (State of matter at room temperature) Liquid (Colour) Red/ orange
Iodine (State of matter at room temperature) Solid (Colour) Grey/ black
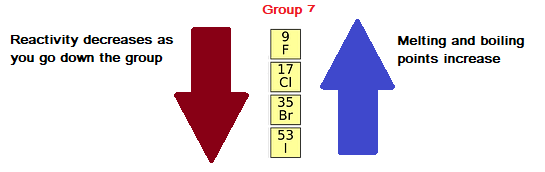
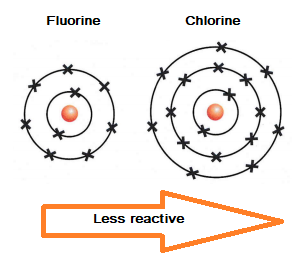
Halogens become less reactive as you go down group 7 in the periodic table, because the outer electron shell gets further away from the attraction of the nucleus, and so an electron is gained less easily.
Displacement reactions of halogens
A less reactive halogen will be displaced by a more reactive one from an aqueous solution of its metal halide.
Chlorine + potassium bromide → potassium chloride + bromine
Cl2 + 2KBr → 2KCl + Br2
Glossary of terms
Halogen – One of the 5 non-metals in group 7 of the periodic table.
Displacement reaction – A reaction in which a more reactive element takes the place of a less reactive element in a compound.
The video below provides an overview of the halogens.

