Circuits, Charge, and Current
This section explains Circuits, Charge, and Current, covering: Circuit Symbols, Electrical Charge and Current and Current and Time Equation.
Circuit Symbols
In circuit diagrams, standard symbols are used to represent electrical components. Some key symbols include:
Image
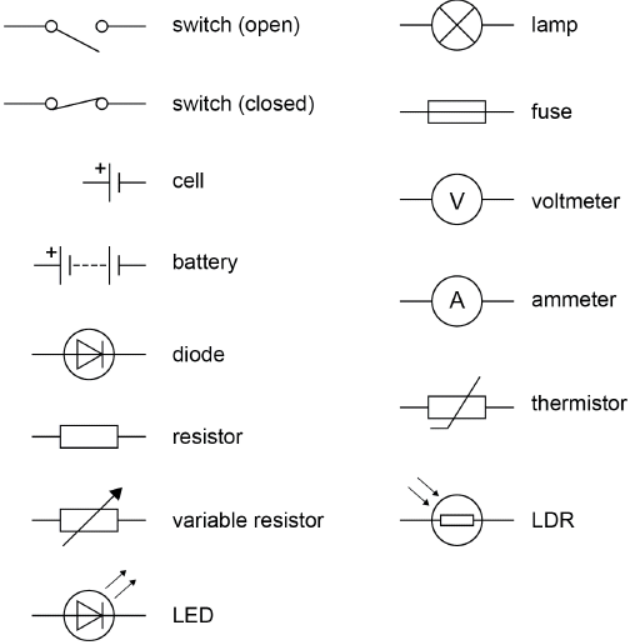
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cell | Provides energy to the circuit. |
| Battery | Two or more cells connected together. |
| Resistor | Limits the flow of current. |
| Variable Resistor | Adjusts resistance in the circuit. |
| Lamp (Bulb) | Lights up when current flows through it. |
| Switch (Open) | Breaks the circuit (no current flows). |
| Switch (Closed) | Completes the circuit (current flows). |
| Ammeter | Measures current in amperes (A). |
| Voltmeter | Measures voltage in volts (V). |
| Diode | Allows current to flow in one direction only. |
| Light-Emitting Diode (LED) | Emits light when current flows. |
| Fuse | Breaks the circuit if current is too high. |
Understanding circuit symbols is important for interpreting and drawing circuit diagrams.
Electrical Charge and Current
- Charge (Q) is measured in coulombs (C). It represents the amount of electricity carried by electrons.
- Current (I) is the rate of flow of charge and is measured in amperes (A).
- Current flows from the positive to the negative terminal in a circuit (conventional current), but electrons actually flow from negative to positive.
Electric Current and Charge Flow
- When a circuit is complete, electrons move through the wires, creating an electric current.
- Current is the same at all points in a series circuit.
- In a parallel circuit, the total current is shared between branches.
Current and Time Equation
The relationship between charge, current, and time is given by:
$$Q = I \times t$$
Where:
- Q = charge (coulombs, C)
- I = current (amperes, A)
- t = time (seconds, s)
Example Calculation
A current of 3A flows for 5 seconds. How much charge passes through the circuit?
$$Q = I \times t = 3A \times 5s = 15C$$
Answer: 15 coulombs of charge flow through the circuit.
Summary
- Circuit symbols help represent components in electrical circuits.
- Charge is measured in coulombs (C) and represents the movement of electrons.
- Current is the rate of flow of charge and is measured in amperes (A).
- The equation $Q = I \times t$ links charge, current, and time.
