UK Electricity Domestic Uses and Safety
This section explains UK Electricity Domestic Uses and Safety, covering: Direct and Alternating Current (DC & AC), UK Mains Electricity, UK Plugs and Why They Are the Safest in the World and Insulation, Fuses and Circuit Breakers.
Direct and Alternating Current (DC & AC)
Electricity can flow in two different ways:
- Direct Current (DC): The electric charge flows in one direction only. DC is supplied by batteries and cells, such as those used in torches and remote controls.
- Alternating Current (AC): The direction of the electric charge reverses periodically. AC is used in mains electricity because it is more efficient for transmitting power over long distances.
UK Mains Electricity
- In the UK, mains electricity operates at a voltage of 230V and a frequency of 50 Hz (50 cycles per second).
- AC electricity is used in homes because it can be easily transformed to different voltages using transformers.
UK Plugs and Why They Are the Safest in the World
The UK three-pin plug is designed with multiple safety features, making it the safest plug globally.
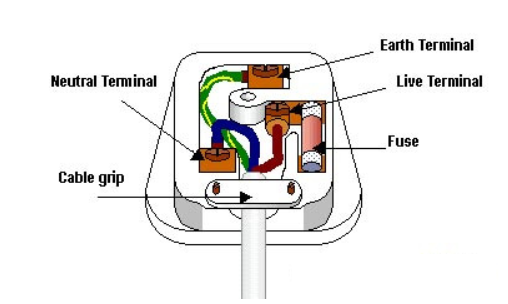
Features of a UK Plug
- Live Wire (Brown) – Carries the 230V AC supply.
- Neutral Wire (Blue) – Completes the circuit by returning the current to the power station.
- Earth Wire (Green/Yellow) – A safety feature that prevents electric shocks by directing excess current into the ground if there is a fault.
- Fuse – Protects the appliance by breaking the circuit if the current is too high.
- Cable Grip – Secures the wires inside the plug to prevent them from being pulled out.
Why are UK plugs the safest?
✔ Earth wire protects users from electric shocks.
✔ Fuse prevents excessive current from damaging appliances or causing fires.
✔ Insulated pins reduce the risk of accidental contact with live parts.
✔ Three-pin design ensures the earth connection is made before the live connection when plugging in.
Insulation, Fuses and Circuit Breakers
Insulation
- Electrical appliances are double insulated if they have plastic casings (e.g., hairdryers), meaning they do not require an earth wire.
- Wires are covered in plastic insulation to prevent electric shocks.
Fuses
A fuse is a thin wire inside the plug that melts if the current is too high, breaking the circuit and preventing fires or damage.
- Common fuse ratings: 3A, 5A, 13A (chosen based on the power of the appliance).
- A blown fuse must be replaced with one of the correct rating.
Circuit Breakers
- More advanced than fuses, as they detect high currents and switch off the circuit faster.
- Unlike fuses, circuit breakers can be reset rather than replaced.
- Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCBs) detect small current changes and are more sensitive than fuses, helping to prevent electric shocks.
Summary
- UK mains electricity is 230V AC at 50Hz.
- Direct current (DC) flows in one direction; alternating current (AC) changes direction.
- UK three-pin plugs are designed with multiple safety features, including fuses and earth wires.
- Insulation prevents electric shocks, and fuses or circuit breakers stop dangerous currents.
