The stages of Glycolysis, the Link reaction and Krebs cycle build up high energy molecules of reduced NAD and reduced FAD.
NAD = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
FAD = flavin adenine dinucleotide
These nucleotide-based molecules are used to make ATP in Oxidative Phosphorylation.
These are both Co-enzymes
Co-enzyme = a prosthetic group to an enzyme which is also known as a Cofactor
Usually a co-enzyme is a Vitamin
(flavin - riboflavin nicotinamide - niacin}
These co-enzymes or cofactors, will accept Hydrogen atoms hence, they become reduced
The H atom, with its electron, is the key to the energy used in Oxidative Phosphorylation because Hydrogen is stripped from reduced NADH and reduced FADH.
The electron e- is passed down a chain of carrier molecules. It releases more energy and generates more ATP
The energy released by this can be used to add Pi to ADP making ATP.
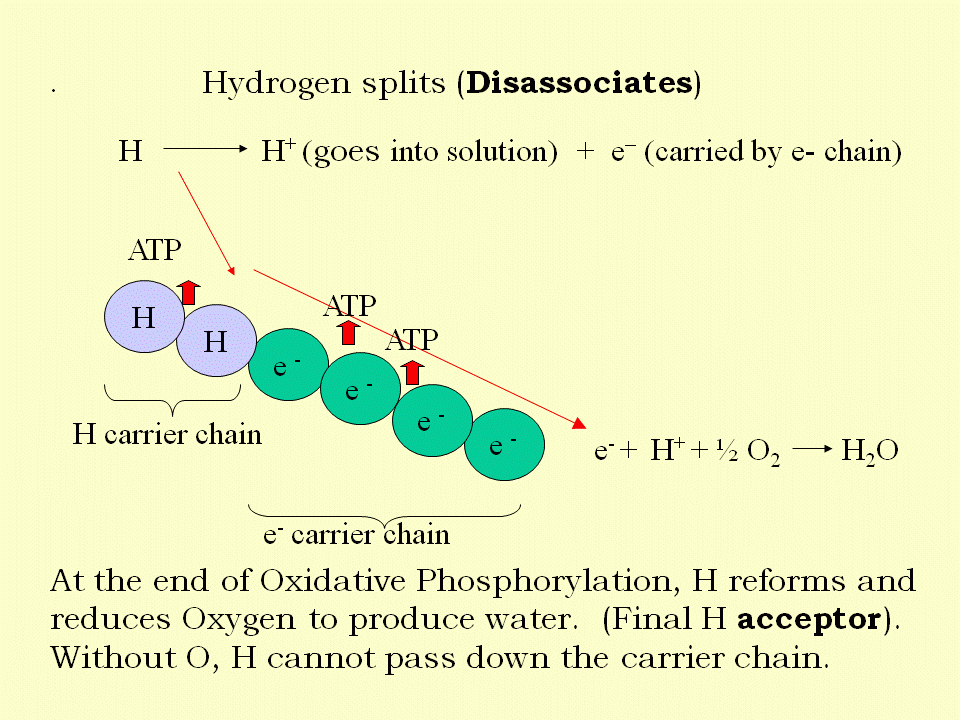
What happens to H?
H is split into H+ and e–. This is termed disassociation – it disassociates
The electron of course passes down a chain of carrier molecules whilst the H+ goes into solution to be ready to reform.
It reforms by reducing O (oxygen) and this becomes H2O.
Thus oxygen is required only at the end of this process as the final acceptor of H+.