Respiratory Quotient (RQ)
The RQ is the ratio of CO2 : O2
RQ = volume of CO2 evolved / volume of O2 absorbed
or
moles or molecules of CO2 evolved / moles or molecules of O2 absorbed
The equation shows that a given volume of carbon dioxide is produced from respiration.
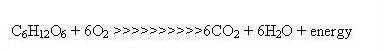
This volume equals that of oxygen consumed.
These values relate to the respiration of carbohydrates.
RQ =
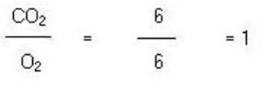
Different respiratory substrates result in different RQ values.
- Physical measurements of oxygen intake against carbon dioxide output can give information about the nature of the substrate being used for respiration.
- Such information can supply an idea of the metabolic rate or activity of an organism.
- The metabolic rate can be calculated by measuring the rate of oxygen consumption.
Tripalmitin is a typical fat. The RQ for this fat is 0.70 because to use this fat, the value of CO2 is 51 (51CO2) whilst the value of O2 is 72.5 (72.5O2). 51 / 72.5 = 0.70.
Thus a considerably greater volume of oxygen is required to metabolise a fat than a carbohydrate but, proportionally less carbon dioxide is evolved. HEAT is released in greater kJ with oxidation of fats than of carbohydrates.
