Coordination is all about the Nervous System & the Endocrine or hormonal system.
Each system works by sending messages according to various stimuli.
- The nervous system operates by means of electro-chemical impulses whilst the endocrine system operates by means of chemical messengers.
Electrochemical impulses from the nervous system rely on a medium to transmit & carry these signals. This is achieved by neurone structure & axons. Axons are like electrical wiring: they have an insulating coating called myelin & operate by a system of negative & positive ions.
The endocrine system produces & secretes hormones which can be proteins. These are the chemical messengers. The endocrine system uses the blood to transport its messengers; this is a much slower process than electrochemical signals.
- Electrochemical impulses are targeted to the particular location that received a stimulus. The sensation produced by a stimulus, such as a pin prick to the finger, stays in that place. The sensation is felt fast in response to the stimulus & fast in receding.
Only if the stimulus continues (someone standing on your toe & not getting off your toe) will the sensation keep being felt. Each time the stimulus detected a wave of impulses pass along the neurones & a sensation is felt: more impulses > more sensation > longer sensation.
Question: Can you outline the organisation of the central nervous system (CNS) & peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
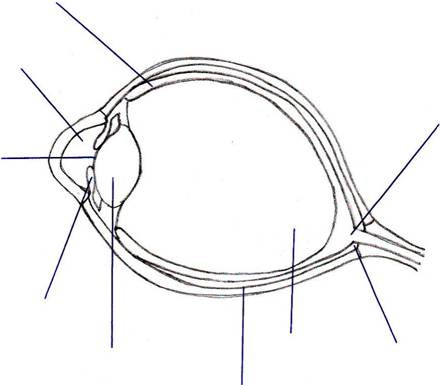
Here is an example of what to expect to be asked: The Eye
- Practice writing a description of a sensory receptor making sure you say that it converts a different form of energy (light energy) into nerve impulses & that you refer to the rod cell in the retina.
Optometrists measure eye function so that they can diagnose a number of conditions.
- Have you had an eye test? This is what happens: the optometrist makes an assessment of receptor activity through routine eye tests. This includes visual acuity, colour vision & response of pupil. The pupil is controlled by muscles.
Medical staff can identify levels of consciousness by using blink/iris reflex tests. These are reflex actions.
So, be able to describe the structure of the eye & outline the functions of its parts including the structure of the retina: rods, cones, bipolar cells & ganglion cells. See diagram at the bottom of this page. Use a text book to identify the parts indicated by labelling lines!