The Sum of Two Vectors
The sum, or resultant, of two vectors such as two forces acting on a single object is the single vector that could replace the two and have the same effect.
There are three steps to finding the sum of two vectors. These are illustrated by working out the sum of a 2 N force acting up the page and a 3 N force acting from left to right, both forces acting on the same object.
Image
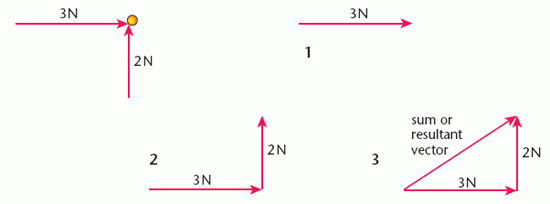
- Draw an arrow that represents one of the vectors in both size and direction.
- Starting where this arrow finishes, draw an arrow that represents the second vector in size and direction.
- The sum, or resultant of the two vectors is represented (in both size and direction) by the single arrow drawn from the start of the first arrow to the finish of the second arrow.
In the example given, the size of the resultant force is 3.6 N and the direction is at an angle of 34° to the 3 N force. These figures were obtained by scale drawing.
