Speed & Velocity
Information about the speed of an object only states how fast it is moving; the velocity also gives the direction. For an object moving along a straight line, positive (+) and negative (–) are usually used to indicate movement in opposite directions. As long as it is moving, the distance travelled by the object is increasing, but its displacement can increase or decrease and, like velocity, can have both positive and negative values.
- displacement is a vector quantity; it specifies both the distance and direction of an object measured from a fixed point.
The diagram shows a distance–time graph and a displacement–time graph for the same motion.
The fixed point is usually the starting point of the motion or the object’s rest position.
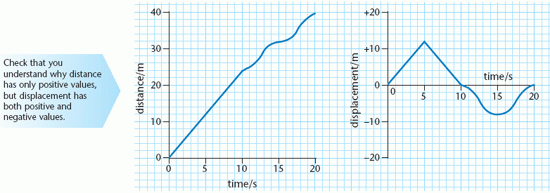
Information from the graphs can be used to calculate the average speed and average velocity over any time period, using the relationships:
average speed = distance travelled ÷ time taken v = Δd ÷ Δt
average velocity = displacement ÷ time taken v = Δs ÷ Δt
The same symbols are used for speed and velocity. When an object is changing speed/velocity, u is often used for the initial speed/velocity, with v being used for the final speed/velocity. The symbol c is usually reserved for the speed of light.
These show that:
- over the 20 s time period, the average speed is 2 m s–1 and the average velocity is 0
- the average speed is constant for the first 10 s, after which it changes.
Calculations of the average speed or velocity over a period of time do not show any changes that have taken place. Instantaneous values are defined in terms of the rate of change of distance or displacement and are represented by the gradients of the graphs.
instantaneous speed = rate of change of distance. It is represented by the gradient of a distance–time graph.
instantaneous velocity = rate of change of displacement. It is represented by the gradient of a displacement–time graph.
The gradient of a displacement–time graph can have either a positive or a negative value, so it shows the direction of motion as well as the speed.
