Covalent Bonding
This section covers Covalent Bonds. Covalent bonds are bonds that will only occur between two non-metal atoms. Covalent bonded atoms share a pair of electrons so that each atom ends up with the outer shell of electrons.
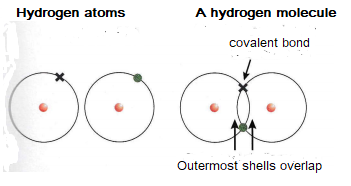
The formation of a covalent bond between two hydrogen atoms.
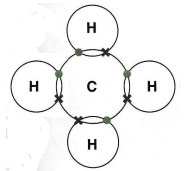
The covalent bonding in methane, CH4. The hydrogen atoms share electrons. The carbon atom shares four pairs of electrons. They do this by sharing a pair of electrons in a single bond.
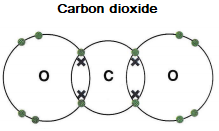
Double covalent bonds occur when two pairs of electrons are shared between atoms, for example in carbon dioxide.
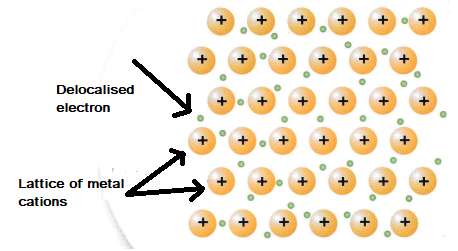
Metallic bonding
Metal consists of large structures. Each atom loses its outer shell electrons and these electrons become delocalised, i.e. they are free to move through the structure. The metal cations are arranged in a regular lattice pattern (see the diagram below).
The video below explains covalent bonding:
You can find more information on Ionic bonding here
