Ionic Bonding
This section covers ionic bonding. Chemical bonding consists of ionic bonding, covalent bonding and metallic bonding.
Ionic Bonding
An ionic bond is the electrostatic force of attraction between two oppositely charged ions (called anions and cations). Ionic bonds can occur between metals and non-metals.
Ionic bonds are formed when metal atoms transfer electrons to non-metal atoms. This is done so that each atom forms an ion with a full outer shell of electrons.
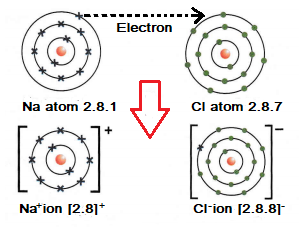
Example 1: The formation of an ionic bond between chlorine and sodium.
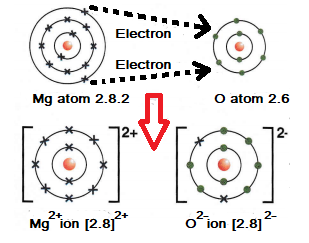
Example 2: The formation of the ionic bond between oxygen and magnesium.
Glossary of terms:
Ion – An atom or group of atoms that has gained or lost one or more electrons in order to gain a full outer shell.
Anion – A negative ion.
Cation – A positive ion.
Delocalised electrons – Free-moving electrons.
The video below explains ionic bonding:
You can find more information about covalent bonding here
